INSEWING - Development of a robotic manipulator of human tubular tissues for suture and support in anastomosis surgery interventions
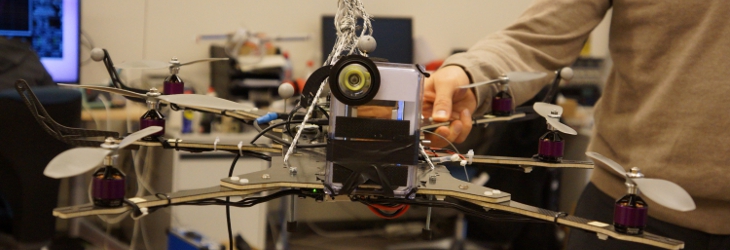
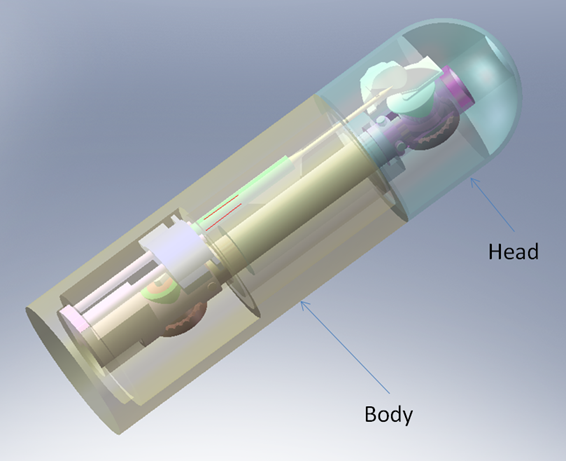
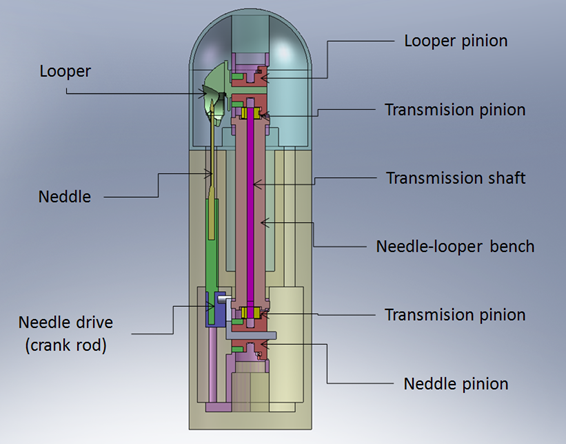
The aim of the INSEWING project is to develop a surgical robotic manipulator device, focused on the improvement of surgical interventions with anastomosis. These interventions consist basically of a cross-cutting of tubular tissue (usually the intestine), removing a piece of it, and re-uniting the remaining ends. This is a common procedure in the treatment of colon cancer which has a high rate of occurrence in the population of the Western Hemisphere.
INSEWING addresses the ECHORD research focus “mobile manipulators and cooperation“, within the scenario “human-robot co-worker”.
It is expected that this innovative new surgical device technology will significantly contribute to the increase of life expectancy in the population. The success of the study, development, and implementation of the new sewing robot will have a very positive social impact – not only for patients, but also for the national Health Departments. The goal is to achieve better results for the patient, techniques used today, in stopping the progression of the disease and in the quality of life after the intervention. The patient will not have all the common complications of traditional anastomosis interventions, like staples rejection by the body, and bowel or dehiscence. This reduction of post-procedural complications means a reduction of time spent in hospital. Additionally, it not only results in speedier recovery of the patients, but also in lower costs for the Health Department.
 |
 |
| Size | Modified | |
| bodyhead.png | 306 KB | 2012/02/07 |
| bodyhead2.png | 234 KB | 2012/02/07 |
| Device in process of sewing.png | 126 KB | 2012/03/19 |
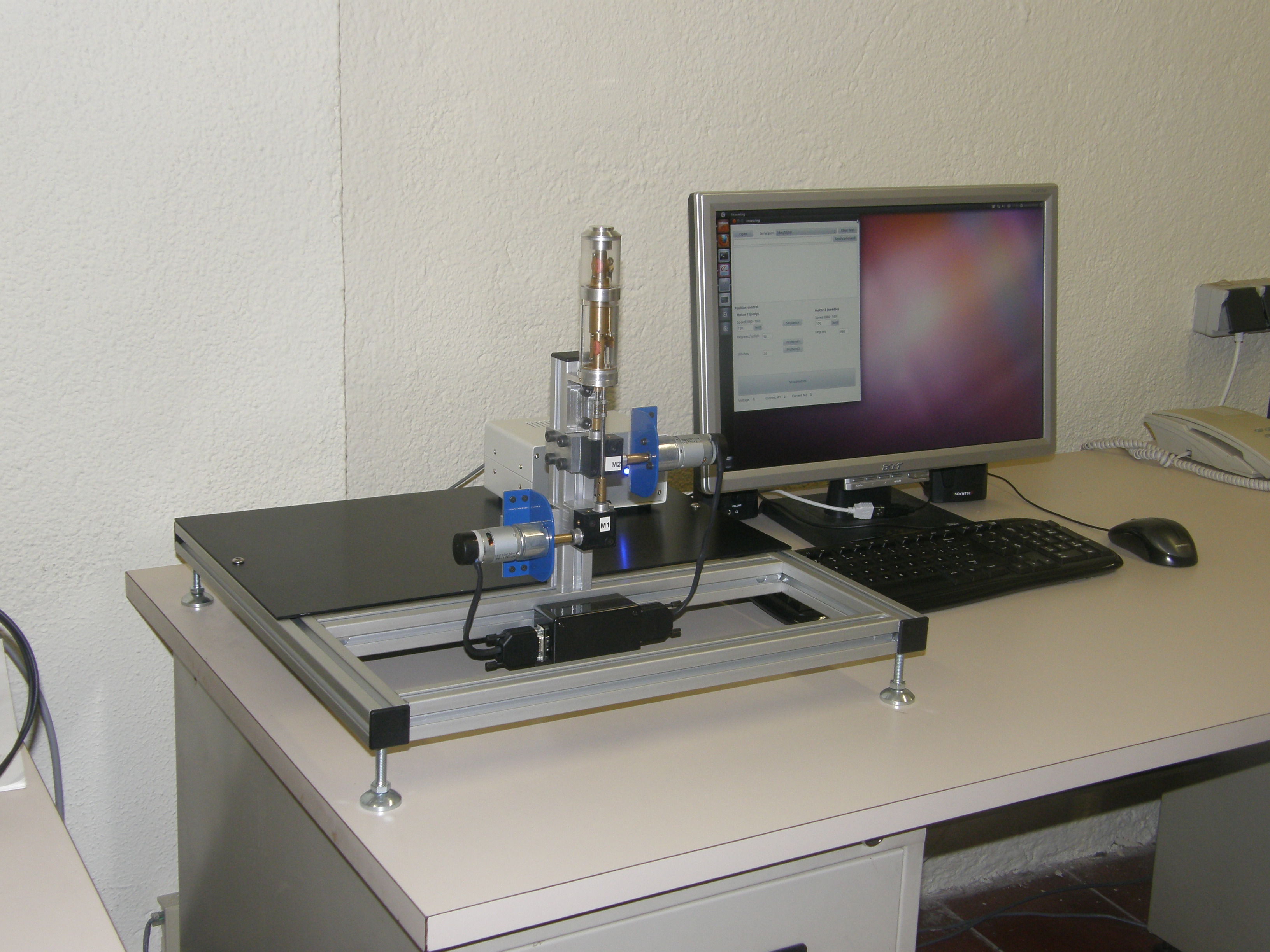
| Insewing_workbench with device.JPG | 1.53 MB | 2012/02/07 |
Experimenting Partners
Universitat Politècninca de Catalunya (Coordinator)