Sep 1, 2011 , by
Public Summary Month 8/2011
The scientific activities carried out during the last two months (M7-M8) can be summarized as follows:
- Identification and implementation of the technique, suitable for MAAT project purposes, able to reconstruct human arm kinematics. It relies on the joint use of 2 magneto-inertial sensors located on the patient arm and position sensors embedded in the robot (Fig. 1).

- The system for monitoring the patient physiological state has been completed. It relies on sensors able to measure pulse, galvanic skin response, respiration and skin temperature (Fig. 2). The monitoring system has been tested on ten volunteer healthy subjects.
- Implementation in a simulated environment of a new control system grounded on a submovement-based trajectory planner that allows adapting robot accuracy and interaction force in unstructured environment (Fig. 3
 ). A comparison with a traditional PD torque control has also been carried out.
). A comparison with a traditional PD torque control has also been carried out. - The effect of vibrotactile stimulation will be evaluated. We are defining the experimental protocol.
- In order to deliver motor tasks of daily living activities during the robotic therapy and motivate the patient, a virtual realty environment has been developed (Fig. 4). The system adapts the performance according to residual ability of the patient.
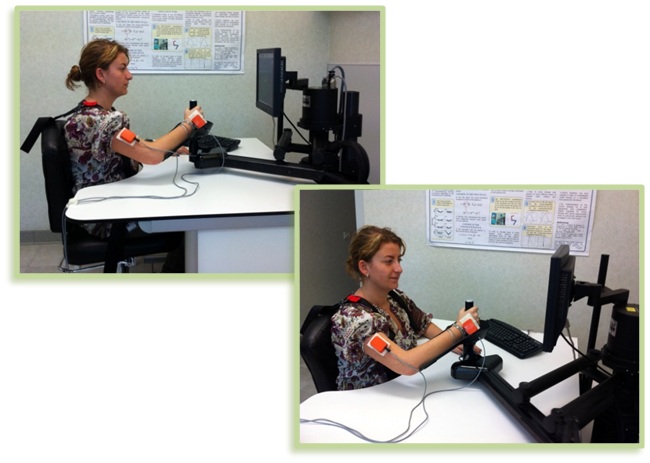

Fig.1. - Arm kinematic reconstruction set-up: the subject performs the exercise with MIT-Manus system; the magneto-inertialsensors placed on upper arm and hand measure radial acceleration and orientation respectively.

Fig.2. - Physical/coordination task (top); Cognitive task (middle); Physical/coordination + Cognitive task (bottom)
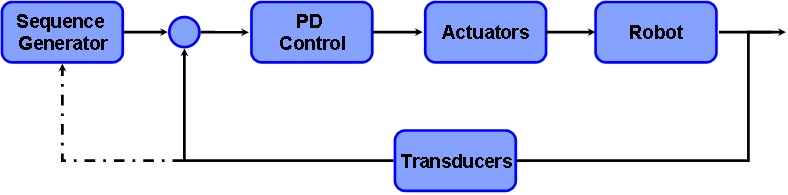
Fig.3. - Block scheme of the control based on submovement composition
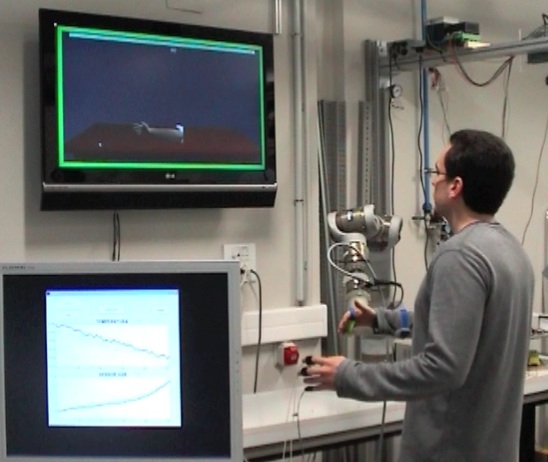

Fig.4. - The Virtual Reality environment reproducing activities of daily living
Aug 2, 2011 , by
Public Summary Month 6/2011
The activities carried out during the last two months (M5-M6) can be summarized as follows:
- Evaluation of different techniques to reconstruct human arm kinematics. Identification of the most suitable for MAAT purposes.
- Definition of a setup for patient physiological state analysis. Planning of tests to evaluate its performances.
- Evaluation of a vibrotactile stimulation system to increase patient motivation.
- Definition of a new controller grounded on a submovement-based trajectory planner that allows adapting the interaction force to the patient residual abilities and a PD torque control.
- Progress on the development of the immersive virtual reality system.
- Publications in international journals and conferences can be found in the public web site of the MAAT project (http://hal.umh.es/maat/Publications.html). Dissemination activities have been promoted also by means of the organization of one workshop and one journal special issue.
Apr 22, 2011 , by
Public Summary Month 4/2011
Main activities carried out during the first 3 months of the MAAT project (http://hal.umh.es/maat) are summarized in the following:
- Identification of the equipment for monitoring patient behavioral and physiological state
- Development of data processing techniques for analyzing patient kinematic and dynamic parameters (Zollo et al, 2010), (Zollo et al, 2011).
- Preliminary activities on the development of the adaptive interaction control system for the rehabilitation robot, based on nonlinear oscillators (Salerno et al., 2011).
- Development of the rehabilitation robot based on Schunk PRL modules
- Development of an immersive virtual reality system that will be dynamically modified according to the patient’s physiological reactions to the given robotic therapy (Morales et al, 2010).