Dec 7, 2011 , by
Public Summary Month 11b/2011
Task 3
During the first all-over motion test, we find out that the load torque of some drive motors reached a critical value. The reason here was the high friction in the Bowden cables and in the rope lead-throughs. To reduce the friction influence, we assembled Teflon coats over the related ropes for better frictional properties. After that we ran a new all-over motion test. This time, the loads of the drives were obviously lower.
Now, the entire robotic arm and its compact drive unit is completley built-up and finalized. The ALEXA robotic system is shown by Figure 1 to Figure 4.
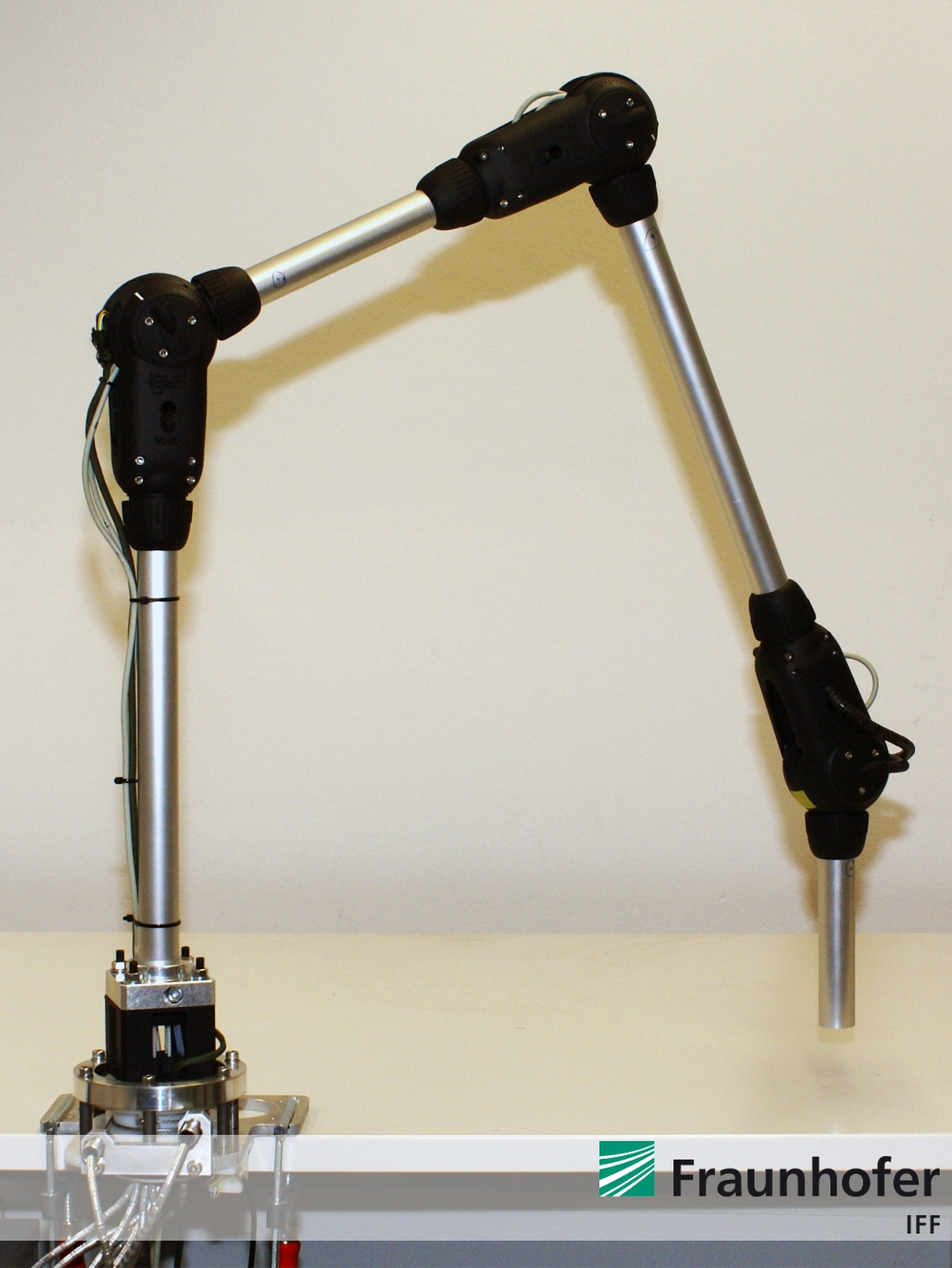

Figure 1: ALEXA robotic arm
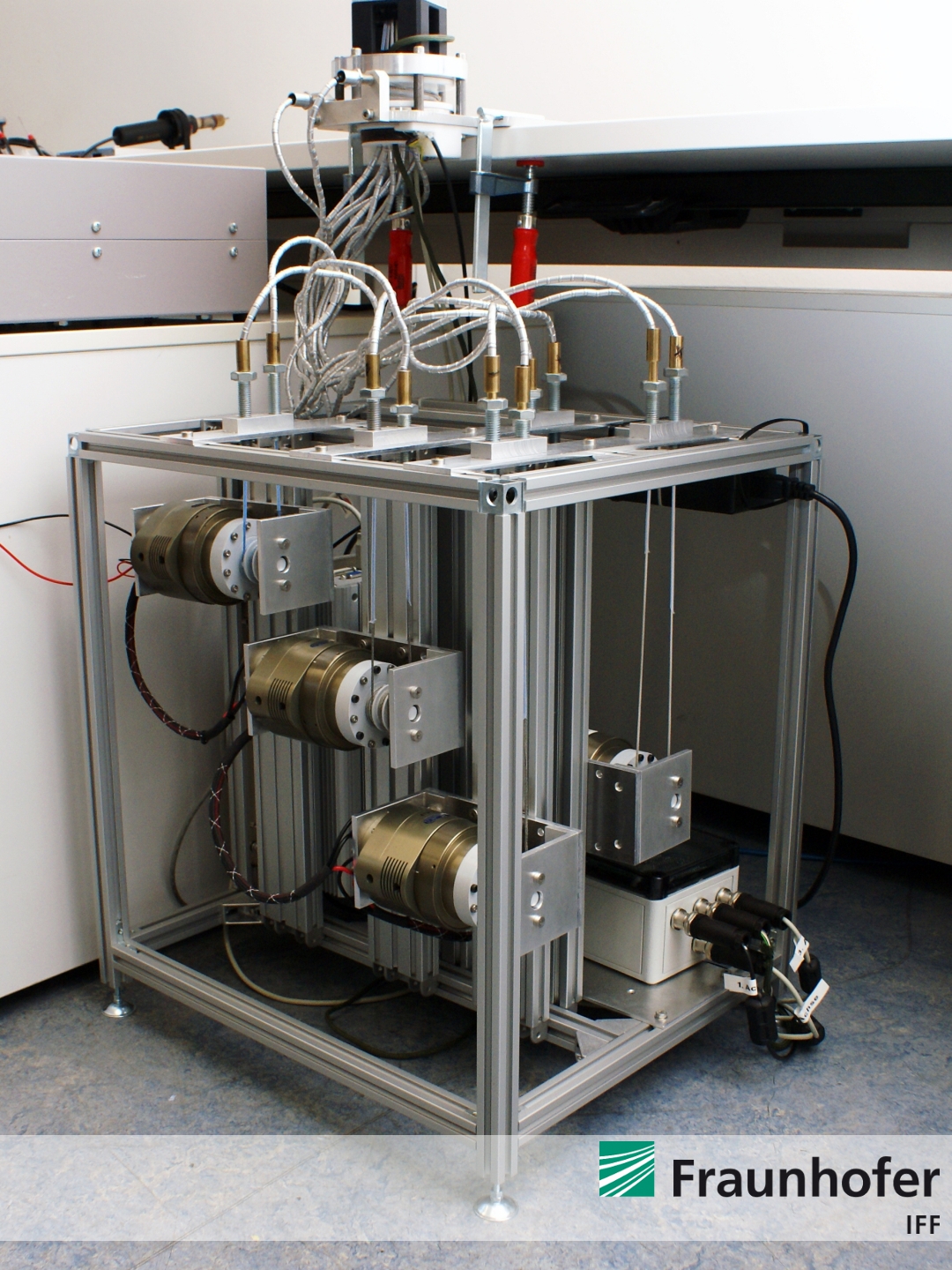
Figure 2: Compact drive unit
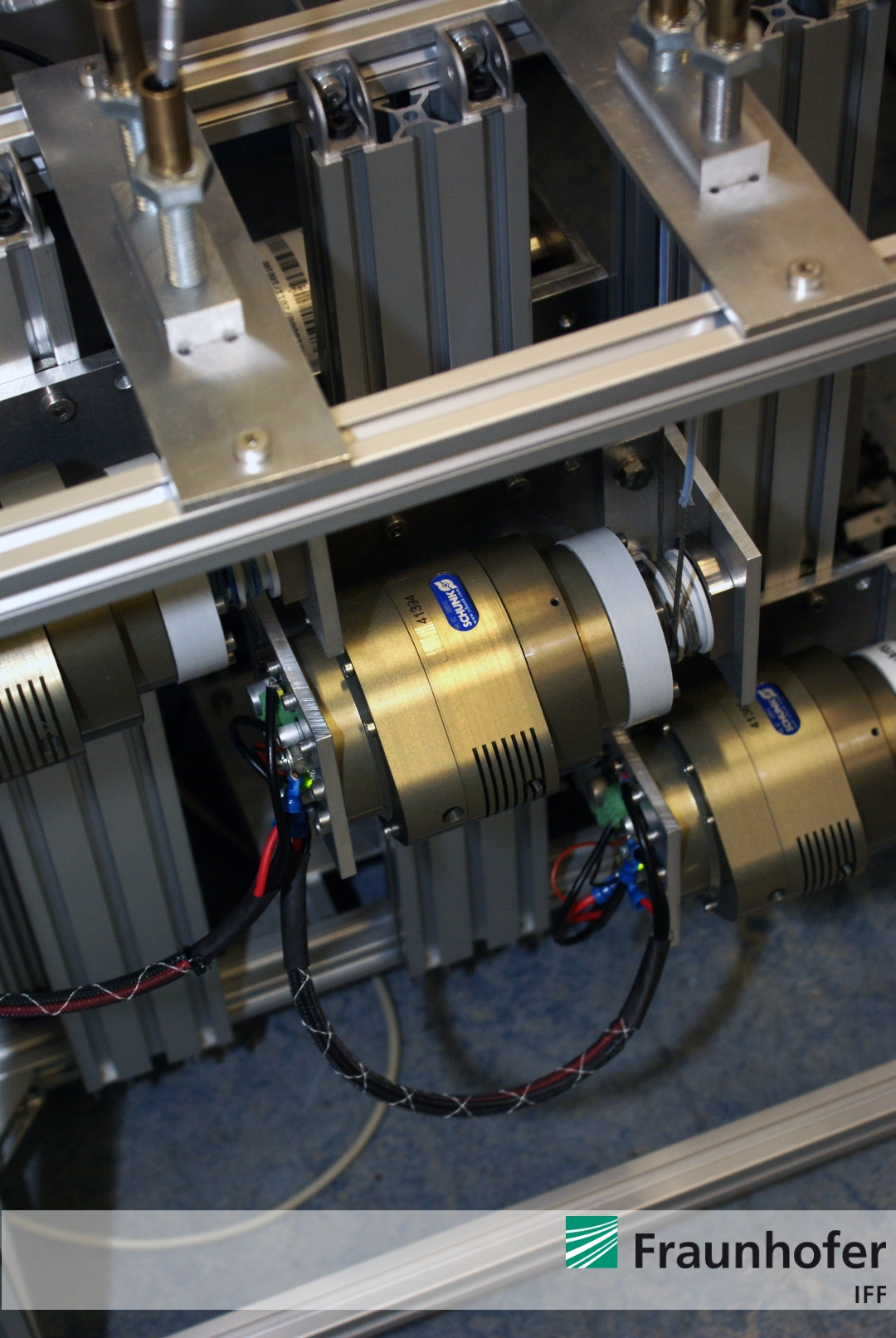
Figure 3: Detailed view of the rope actuating drives manufactured by Schunk
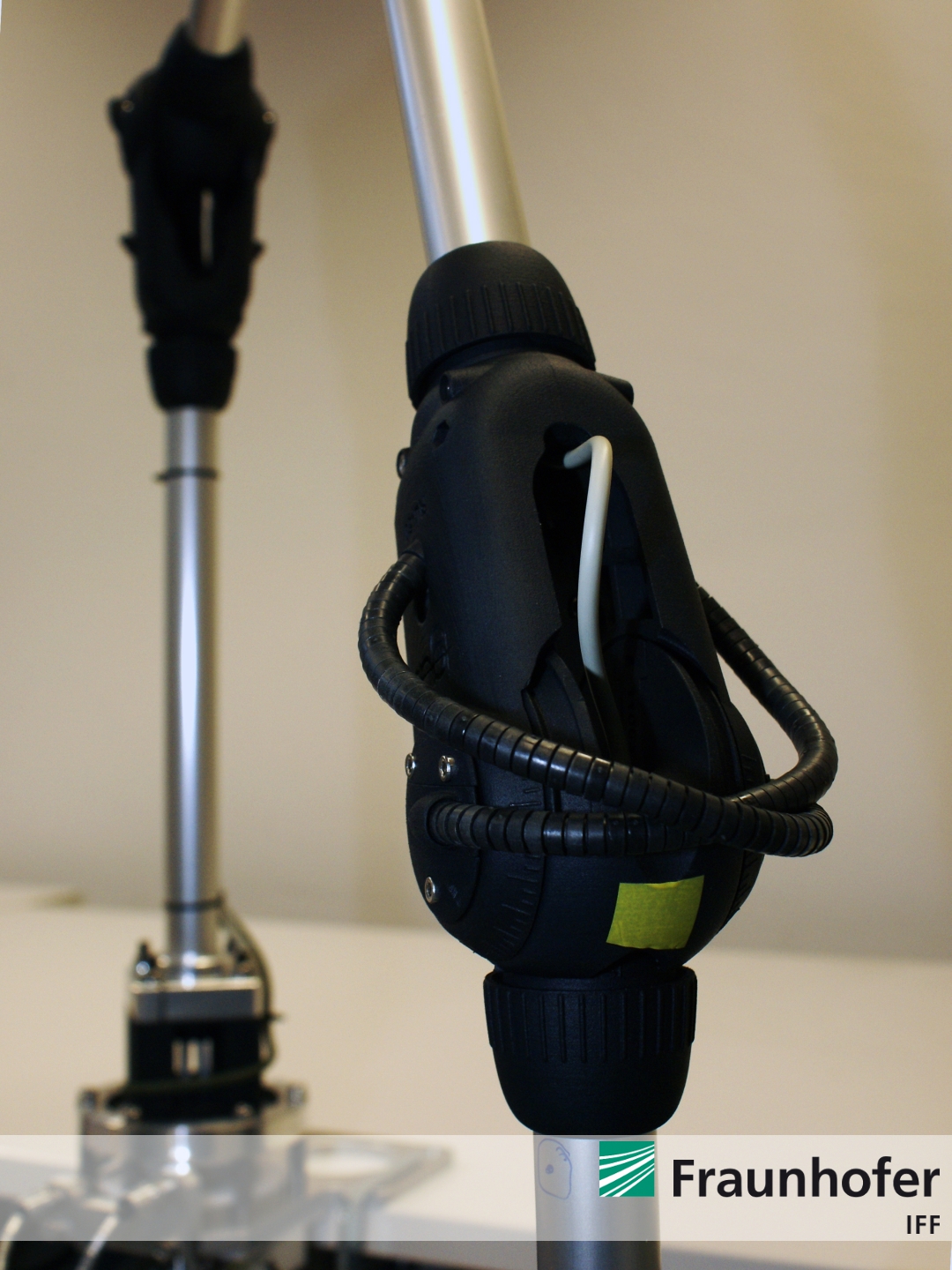

Figure 4: Wrist joint
Further, we constructed a lightweight gripper that can be actuated by a rope. The gripper is made out of Polyamid 12 and was produced in Rapid Prototyping techniques. Furthermore, we used compliant fingers with FinRay design manufactured by Festo. A socket for the camera was also integrated.
Task 4
The implementation of the main control system is almost finished. The main control system includes a software system that controls the drive motors, plans optimized trajectories, acquires all sensor data and avails image processing interfaces. Now, we debugging all software parts and searching for optimization potentials.
Task 5
We began to prepare all existing software modules for image processing and object recognition to link with the interfaces of the main control software. After debugging and optimizing the main control software is finished we will implement the visual servo control algorithms.